Ankylosing spondylitis
HLA-B*27 gene/antigen
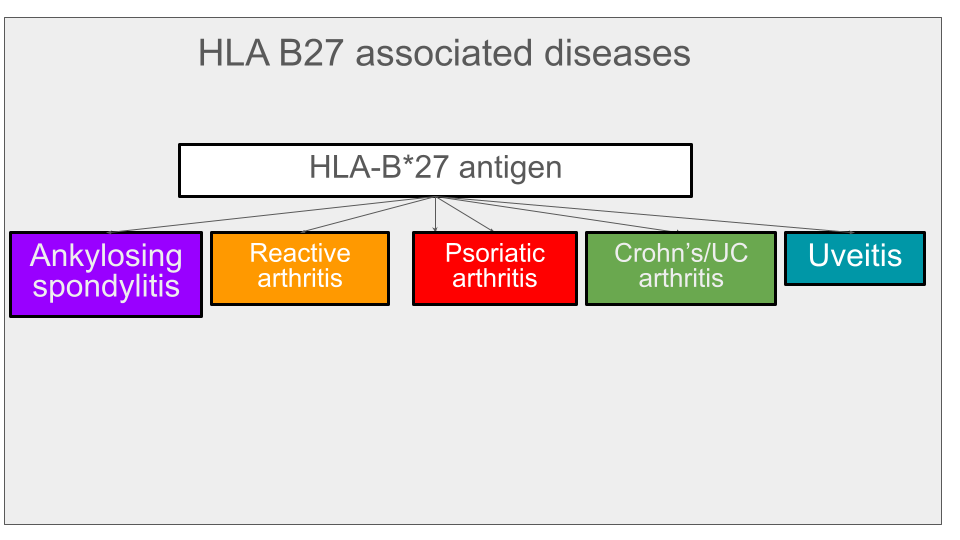
Present in 8% of the population. In 90% of cases of AS. Present in 50% of reactive arthritis. Associated with other disease but only present in a minority of patients with psoriatic arthritis, Crohn's arthritis or uveitis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Ankylosing spondylitis
Inflammatory back pain questionnaire
Imaging
X-ray spine
A series of plain (conventional) radiographic changes characteristic of AS can develop progressively over the course of disease; these are best seen on the lateral view:
Squaring of the vertebral bodies due to anterior and posterior inflammation and bone erosion and deposition is a relatively early radiographic sign of spinal involvement in AS.
Changes that are more easily distinguished and found at later stages of AS include syndesmophytes and ankylosis of the facet joints. When syndesmophytes from a lower and an upper vertebra join together, they become a bridge. Syndesmophytes may very infrequently (fewer than 5 percent) be present in the absence of radiographic sacroiliitis.
The signature abnormality that is most easily recognizable is the bamboo spine in late AS. Unlike in AS, syndesmophytes of the spine are rare in patients with nr-axSpA
MRI L spine
Abnormalities of the spine on MRI are not used in the routine diagnosis of axSpA. However, it is most useful when pathology other than SpA is suspected. MRI of the more painful areas of the spine may be helpful in the small number of patients in whom an expert has a high level of suspicion for nr-axSpA (eg, patients with clinical features strongly suggesting SpA with normal or uncertain SI joint radiography) but in whom MRI of the SI joints is normal. MRI of the spine may also be useful in patients with severe pain in the spine of uncertain etiology and for assessment of disease activity in selected patients. MRI of the spine should cover the part of the spine with the most severe symptoms. For evaluating spondylitis, only the sagittal plane is necessary. The MRI slices should include the entirety of the vertebral bodies being imaged and the facet joints. The spinal lesions that may be seen in patients with axSpA result in either BME observed with the STIR or the T2-weighted sequences with fat suppression, or areas of fatty deposition observed as high-intensity lesions in the T1-weighted sequences. A 2012 consensus of opinion on what spinal lesions on MRI are typical of spondylitis by the ASAS/Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) MRI working group was that a positive spinal MRI for inflammation can be defined as the presence of anterior or posterior spondylitis in at least three sites, as the finding of single vertebral lesions is relatively nonspecific . Subsequent studies showed that more than three inflammatory lesions were necessary to provide sufficient specificity and that the presence on MRI of the spine of either at least five inflammatory lesions or at least five fatty lesions resulted in specificity of at least 95 percent.[1]
Coding
ICD 10 code = M45.9
M45.9 Ankylosing spondylitis
M45.2 Ankylosing spondylitis of cervical region
M45.4 Ankylosing spondylitis of thoracic region
M45.6 Ankylosing spondylitis of lumbar region
Associated diseases/complications
Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with higher lymphoma risk. Is ankylosing spondylitis? Lymphoma is more common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis whether treated or not and I do not know if this is true for ankylosing spondylitis patients. One patient's doctor at MD Anderson told him that he did not think his TNFI drug caused his lymphoma and permitted taking it if needed. Per Ann Rheum Dis 2013: "SIRs for lymphomas were based on 29 events from RA, one from AS. The number of lymphomas observed in RA studies was significantly greater than expected compared with a US-based age- and sex-matched population (standardized incidence rate (SIR)=2.74; 95% CI 1.83 to 3.93)." SIR for ankylosing spondylitis was 1.93.
Differential diagnosis
Diffuse skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
Monitoring
BASDAI BASFI
How to calculate a BASDAI. Add scores of 1-4 = A. Avg of scores 5-6 = B. A+B/5= BASDAI
Treatment
Adalimumab (Humira;Amjevita;Hyrimoz)
Dose for AS is reserved for patients who do not have an adequate response to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs); may continue NSAIDs and/or analgesics. SUBQ: 40 mg every other week. [2]
Cimzia
Cimzia PI
Rinvoq
Xeljanz
Remicade
Enbrel
Taltz
Definitions
Saggital = The sagittal plane also known as the longitudinal plane is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divide it into two equal parts (mid-sagittal), or away from the midline and divide it into unequal parts (para-sagittal). See Wikipedia
Syndesmophyte = A bony growth originating inside a ligament, commonly seen in the ligaments of the spine, specifically the ligaments in the intervertebral joints leading to fusion of vertebrae. Syndesmophytes are pathologically similar to osteophytes. Ankylosing spondylitis patients are particularly prone to developing syndesmophytes. They are also commonly seen in patients who have had back surgery or other chronic stresses on the ligaments of their spine. Syndesmophytes indicate spine degeneration, similar to osteophytes of spine; however, they bridge across the joint as compared to osteophytes which are non-bridging. See Wikipedia
References
[1] D Yu, A Vantubergen. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis) in adults. Uptdate
[2] Adalimumab (including biosimilars): Drug information. Uptodate